SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
SPECIAL ISSUE
Area of Article : ALL

SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
SPECIAL ISSUE

SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.1 IPRP-19
Awareness about copyright
and Intellectual property right has been developed among copyright Intellectual
property right holders and users. The more instance of copyright violation are
observed, there is need to develop understanding among the users to protect the
right of copyright and intellectual property right holders. Information
literacy about fair use among the users Needs to be developed. The library
professionals should also know the provisions of fair use under the copyright
act and should take right steps to protect the interest of copyright holder.
Book piracy has become serious problem to copyright holders. Appropriate
mechanism to protect right of copyright holders and prevention of information
piracy necessary.
Keywords :- Copyright,
Information, Librarianship, Phonographs, Broadcasting and Databases
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.2 IPRP-19

Intellectual property is a
right of creation of their work. This work is classified into Patent,
copyright, trademarks, tradesecrets, right of publicity. The main aim of
Intellectual copyright is to encourage the creation of a large variety of
goods.
Keywords:
Intellectual, patent, copyright, trademarks, trade secrets, publicity.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.3 IPRP-19

A patent is one of the forms
in intellectual property. The object of product law is to encourage scientific
research, new technology and industrial process. The grant of exclusive
privilege to own, use or sell the method or product patented for limited
period, stimulates new inventors of commercial utility. The price of the grant
of the monopoly is the disclosure of the inventing at the patent office, which
after the expiry of the period of monopoly, passes into push domain. An
invention which must be new and a useful. It must have novelty and utility. The
patent are granted to encourage inventions and to secure that the invention are
worked in India on a commercial scale and to the fullest extent that is
reasonable practicable without undue delay. So true inventor required to know
how to ret patent in India and other countries through his self or legal
representative. Without patent no one use, sell and research an invention.
Keywords :-
Patent, patent history, Patent Application, processing an Application, Patenting abroad.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.4 IPRP-19

Govt agencies like NAAC,
NIRF, ARIIA assess and accredit
educational institutions rank and give special attention to explore Intellectual property( IP) Education being
imparted to both students and staff.
Universities and colleges disseminate the knowledge through research carried
out in their laboratories and through teaching. In the era of globalization,
through internet, one can retrieve information just with a click. As far as
teaching and research is concerned, one can use open access publication but
same may not be true for laboratory finding and research. Such findings need to
be confidential so that it can be patented and developed commercially. To
manage the IP derived from their own research, government grant rights to their
IP so that universities and colleges can convert invention in to commercialise
product. This may also lead to
strengthening the industry-institute linkage which is really need of the time. In
the present paper, the need for Institute to understand how to use IP system
and to run a IP center in campus with well defined IP policies is discussed.
Keyword: IP, Patent
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.5 IPRP-19

Intellectual
Property refers to intellectual creativity of a creator. In contrast to
physical property, intellectual property is an intangible asset of a person.
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) is the exclusive rights given to the
creators to their creations. Common types of Intellectual Property Rights are
patents, copyrights, trademarks, industrial deigns, geographical indications,
trade secrets, layout designs for integrated circuits and even ideas.
Intellectual property rights provide an incentive to the creator to develop his
creation and to share it with other people for the development of the society.
The basic aim of the IPRs is to help in meeting the challenges in the
development like reducing poverty, stimulating economic growth, improving the
health status by providing medicines to the poor, improving access to education
and contributing the overall sustainable development. Though IPRs provide
incentive to the author or the creator and lead to a competition in the field
of invention but it is also an intellectual protectionism or a form of a
temporary monopoly enforced by the state.
Keywords: Intellectual Property, Intellectual Property Rights, patents,
copyrights, trademarks, geographical indications.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.6 IPRP-19
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.7 IPRP-19

Intellectual
property (IP) has emerged as a key driver in knowledge economy. The
socio-economic development of a country depends to a large extent on the
creativity of her people and creative works can’t be encouraged without
effective administration of copyright laws. This paper gives an overview
of intellectual property rights (IPR), Types of IPR and brief introduction to
Copyright.
Keywords: IP, IPR, Copyrights,
infringement, Industrial Property
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.8 IPRP-19

Intellectual property rights
(IPR) is a term referring to creations of the mind, such as inventions,
literary and artistic works; designs and symbols, names and images.
Intellectual property rights (IPR) allow their owner to completely benefit from
his/her product which was initially an idea that developed and crystallized.
IPR can be divided in to several types like, copyright, trademark, etc.
Copyright protects written or published works such as books, song, films and
artistic works, patents protects to commercial invention and designs protects
to drawings and computer models.
Keywords: Intellectual
Property Rights, Patent, Copyright.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.9 IPRP-19

The rapidly changing
scenario and India’s continuing progress towards economic upliftment and
globalization through liberalized policy make it imperative that the potential
beneficiaries of the Intellectual Property Right (IPR) system familiarize
themselves with basic elements of IPR to maximize their exploitation. According
to Dr. R. A. Mashelkar, the director General, CSIR (India) in his article
published in journal of chartered Secretary (Jan. 2002) felt that “Twenty first
century will be the century of knowledge. A nation’s ability to convert
knowledge into wealth and social good through the process of innovation, will
determine its future. In this context, Issues like generation, valuation,
protection and exploitation of intellectual property (IP) are going to become
critically important all around the world. Exponential growth of scientific
knowledge, increasing demands for new forms of intellectual property protection
as well as access to IP related information, increasing dominance of the new
knowledge economy over the old brick and mortar economy, complexities linked to
IP in traditional knowledge, community knowledge and animate objects, will pose
a challenge in setting the new 21 century IP agenda.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.10 IPRP-19
Intellectual property, very
broadly, means the legal rights which result from intellectual activity in the
industrial, scientific, literary and artistic fields. Countries have laws to
protect intellectual property for two main reasons. One is to give statutory
expression to the moral and economic rights of creators in their creations and the
rights of the public in access to those creations. The second is to promote, as
a deliberate act of Government policy, creativity and the dissemination and
application of its results and to encourage fair trading which would contribute
to economic and social development. 1.2 Generally speaking, intellectual
property law aims at safeguarding creators and other producers of intellectual
goods and services by granting them certain time-limited rights to control the
use made of those productions. Those rights do not apply to the physical object
in which the creation may be embodied but instead to the intellectual creation
as such.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.11 IPRP-19

In this modern
Information Explosion age the term
Patent was known from long back. Copyright, trademarks and patents were also used in one or another form. These
are all related to the Intellectual product of human mind. Hence, concept of
Intellectual Property Rights covers all types of material or products that
produced from the human mind. Here author intends to discuss Intellectual
Property Rights (IPR) , copyrights, trademark and patent.
Keywords: Intellectual
Property, Intellectual Property Rights, Copyright, Trademarks, Patents, What is
patent, Criteria for filing a patent, Steps for patent application, Adventages
of patents.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.12 IPRP-19

Intellectual property is an
intangible property or proprietary asset, which applies to any product of the
human intellect that has commercial value. Intellectual Property Rights
(I P Rights) are one’s legal rights in respect of the ‘property’ created by
one’s mind – such as an invention, or an artistic work, or piece of music, or a
name or slogan or symbol, or a design, which is used in commerce, in the form
of books, music, computer software, designs, technological know-how, trade
symbols, etc. This paper explain what is Intellectual Property rights, Why
Intellectual Property rights, Types of Intellectual Property rights and need of
Intellectual Property rights.
Keywords:- Intellectual Property rights,
Patent, Copyright
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.13 IPRP-19

India has an ancient and
great tradition of knowledge benefaction. It is considered as the best and
topmost benefaction. India has an intellectual heritage in the fields of
literature, research, intellectual skills in software designing and also in
missile technology. At the initial stage the concept of intellectual property
rights was not rooted very easily in India. But when the news of Basmati Rice
and turmeric patent spread people started to think about the intellectual
property rights. At that time different ideologies came in to existence like
there has been a lot of controversy on the role of intellectual property
rights. Some said copyright is a kind of protectionism it will lead to monopoly
which may be obstacle in public interest and specific needs of the country. The
present paper aims to focus on the importance of intellectual property rights
and infringement of copyright as a violation of intellectual property rights.
The intellectual property rights are territorial rights by which owner can
sell, buy or license his intellectual property similar to physical property.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.14 IPRP-19

Intellectual
property rights are like any other property rights – they allow the creator, or
owner, of a patent, trademark, or copyright to benefit from his or her own work
or investment. These rights are outlined in Article 27 of the Universal
Declaration of Human Rights, which sets forth the right to benefit from the
protection of moral and material interests resulting from authorship of any
scientific, literary, or artistic production. The importance of intellectual
property was first recognized in the Paris Convention for the Protection of
Industrial Property in 1883 and the Berne Convention for the Protection of
Literary and Artistic Works in 1886. Both treaties are administered by the
World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).Intellectual property refers
tocreations of the mind: inventions, literary and artistic works, and symbols,
names, and images used in commerce. Intellectual property is divided into two
categories: Industrial Property includes patents for inventions,
trademarks, industrial designs and geographical indications. Copyright includes
literary works such as novels, poems and plays, films, musical works, artistic
works such as drawings, paintings, photographs and sculptures, and
architectural designs. Rights related to copyright include those of performing
artists in their performances, producers of phonograms, and those of
broadcasters in their radio and television programs.
Keywords: Intellectual Property Rights, Patents, Copyright, trademark etc.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.15 IPRP-19

God gifted a wonderful thing
called Brain to Man and Mother Nature endowed him with the abundant physical
and biological resources on the earth. Man started creating his own world by
application of his brain or mind and by utilization of these natural resources.
Man has also been bestowed with imagination and creativity. With his
imagination and creativity, he has been producing various articles or products
for his needs, comfort and convenience. In the earlier era, the creations and
inventions by him fell in a public domain. These were the common properties.
Anybody could use and copy these creations and inventions without any
restriction, reservation or payment. However, with the passage of time, the
importance and value of these creations was realized. The commercial aspect
started playing a significant role in these creations. By end of Twentieth
Century, the things created and invented by the human mind were recognized as
an intellectual property of the owner .The owner's right over these properties
was accepted and is known as an Intellectual Property Right (commonly called
I.P.R.). A new set of laws called Intellectual Property Right Laws, were
enacted to protect these property rights. These I.P.R. laws provided a
protection to the owners under different categories and names like Patents,
Industrial designs, Copyrights, Trade- Marks etc.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.16 IPRP-19

India, with its rich
heritage is well identified for its unity in diversity. People from different
religion, caste, language and custom live together. Different religions have
different culture, and they follow it with keeping its greatness alive. This is
the only country which has accepted cultural diversities and follows them. Thus
the nation represents ideal integrity. As India has agreed with all the customs
and traditions it becomes the nation of multiculturalism. Multiculturalism is not
only seen in religious ceremonies but also in literary works produced in India.
Indian literature has been produced in various regional languages. Right from
Sanskrit to foreign language like English is being used for creating literary
works. Initially, Bengali writers started translating their Bengali works into
English. Then literary works were being written in English. Other regional
writers also tried their hands in English. Many Indian writers have created
wonderful works in English.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.17 IPRP-19

SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.1 NCNA-19

In the present work, influence of varying particle size of cadmium
ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via ceramic and sol-gel auto combustion
method on the structure and magnetic properties is reported. Cadmium ferrite in
bulk and nanosize form was prepared by ceramic technique using AR grade oxides
of respective ions (CdO and Fe2O3) and sol-gel auto
combustion method using AR grade nitrates of respective ions (Cd (NO3)2
• 6H2O and Fe (NO3)3 • 9H2O). The
X-ray diffraction technique was used to study the structure while pulse
hysteresis loop technique was used to study the magnetic properties. The
analysis of XRD patterns reveals the formation of single phase cubic spinel
structure. The XRD data was used to obtain the particle size. The particle size
of the ceramically and sol-gel synthesized CdFe2O4
calculated using Scherrer’s formula was found to be – nm and – nm respectively.
The lattice constant of both the samples is in reported range. The M-H
hysteresis curve shows remarkable changes in saturation magnetization and
coercivity. Thus, the particle size shows strong influence on the structure and
the magnetic properties of cadmium ferrite.
Keywords: CdFe2O4, ceramic method, sol-gel auto combustion
synthesis, magnetic properties.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.2 NCNA-19
Spinel
ferrite having composition Ni0.33Zn0.63Fe2O4
was prepared by ceramic method and characterized by X-ray diffraction
technique. The magnetic and initial permeability properties were investigated
by standard method. X-ray diffraction pattern analysis confirms the formation
of single phase cubic spinel structure. The saturation magnetization, coercivity
and remenance magnetization properties obtained in the present work are
suitable for multilayer chip inductors applications (MLCI). Temperature
dependence of initial permeability show decreasing trend.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.3 NCNA-19

Zinc sulphide (ZnS)
thin films were deposited on glass substrate using relatively simple chemical
bath deposition. method (CBD), using the mixed aqueous solution of zinc
sulphate, thiourea and ammonia. The ammonia was used as the complexing agents.
The preparative parameters are concentration, pH of solution, deposition time
and temperature has been optimized. Thin films of ZnS with different thickness
100-350 nm were prepared by changing the deposition time from 20–100 minutes at
800C temperature. The effect of film thickness on structural and
optical properties was studied. The thin films were characterized by using
X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transformation, Infrared spectroscopy
(FTIR). The effect of thin films thickness on optical and structural properties
has been studied.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.4 NCNA-19
The dielectric
relaxation study for lorazepam and ethanol binary mixture has been carried out
using the time domain reflectometry (T.D.R.) technique at temperature 283K,
288K, 293K and 298K and at different concentration, in the frequency range of
10MHz to 50Ghz. The dielectric parameters have been obtained from the complex
permittivity spectra. The dielectric parameter shows change with temperature
and concentration. The results obtained are used to interpret the nature and
kind of solute-solvent interaction.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
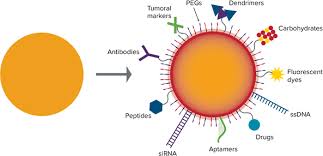
1.5 NCNA-19

Nanotechnology is the
nano-scale-based science and technology. Nanotechnology is the understanding
and control of matter at dimensions of approximately 1to100 nanometers. Nanotechnology
includes various fields; this idea entails its applications to diverse fields
of Biomedical Sciences. Nanoparticles have revolutionary applications for
diagnosis to treatment of various types of diseases. These nano-particles,
nano-rods, quantum dots, nano-wires, and carbon nano-tubes in diagnostics cell labeling, biomarkers, and contrast
agents for biological imaging, drug delivery systems, and nano-drugs are the
advanced uses for treatment of infectious and non-infectious diseases. This
research review tries to summaries the most recent progress in the field of
significance of nanoparticles in field of biomedical sciences for the
empowerment of Bio-Life.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.6 NCNA-19
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.7 NCNA-19
Graphene is a
honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms. Graphene's hexagonal lattice can be regarded
as two interleaving triangular lattices. A topological index for molecular
graph is a numerical quantity which is invariant under automophisms of the
graph. The topological indices can be
obtained from the corresponding topological polynomials. In this paper
augmented polynomial, augmented Revan polynomial, augmented reverse polynomial
and Second hyper-Revan polynomial are investigated for graphene.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.8 NCNA-19
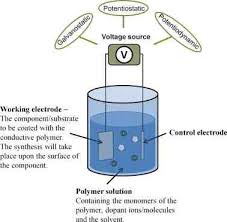
In the present
investigation, electrochemical behavior
of polyaniline (PANI) thin films which is synthesized by galvanostatic technique on platinum
substrate as working electrode in three electrode system. Various process
parameters Viz. applied current density, concentration of dopant and time of
deposition were optimized during the
deposition of PANI thin films. The Surface morphology was characterized by
Scanning probe technique Viz. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) which confirms the
deposition of thin films.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.9 NCNA-19
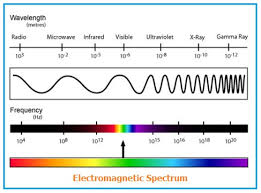
The complex permittivity spectra and
thermodynamic properties of 1,2-dichloroethane (DE) and n,n-dimethylformamide
(DMF) has been obtained at 15°C temperature in the frequency range of 10 MHz to
30 GHz by using time domain reflectometry technique for 11 different
concentrations of the system. A complex spectrum gives information regarding
dielectric dispersion (ɛʹ) and dielectric absorption (ɛʺ), which indicates the
purity of the liquid mixture. In binary mixture of polar liquids mixed
together, there is a change in the energy of the system. This change in energy
can be interpreted with thermodynamic parameters such as free energy of
activation (DG), molar enthalpy of activation (DH) and molar entropy of
activation (DS).
Keywords: Microwave frequency,
dielectric permittivity, dielectric loss, time domain reflectometry and
thermodynamic properties.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.10 NCNA-19
Polyaniline matrix has been investigated .In the present work the
polyaniline matrixes were synthesized by using electrochemical polymerization
technique. The matrix were deposited on platinum electrode using Potentiostatic
Conditions at room temperature. The synthesized matrix were characterized by using electrochemical
technique, conductivity measurement and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).. It
has been observed that the polyaniline matrix behaves like Semiconductor which
could be better structure for immobilization of biocomponent, so that it can be
used for the development of cybernetics.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.11 NCNA-19
The Cd2+ions substituted samples of mixed nickel- copper
ferrites having the compositional combination Ni0.5Cu0.5-xCdxFe2O4
(x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5) have been synthesized using AR grade oxides by
standard solid state reaction technique. The formation of single phase cubic
spinel structure of all the samples under investigation have been carried out
using X-ray diffraction technique at room temperature. Using LCR–Q meter the
dielectric constant (ε′), dielectric loss (ε″), dielectric loss tangent (tand) was measured as a
function of frequency. The frequency dependence of dielectric parameters
measurements was carried out within the range 100 Hz to 1 MHz. The values of
dielectric parameters (e¢,e²and tand)are much higher at lower frequencies but decreases with increase in
frequency. At very high frequencies, its values become so small that it becomes
independent of frequency. The decrease in dielectric parameters with increase
of frequency may be due to the fact that beyond a certain frequency of the
external electric field, the electronic exchange between ferrous and ferric
ions cannot follow the alternating field. It is observed that dielectric
constant (e¢), dielectric loss (e²) and dielectric loss tangent (tand) appreciably increases
with cadmium concentration x but decreases with increases in frequency.
Keywords: Mixed spinel ferrites, XRD, dielectric properties.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.12 NCNA-19

Mixed ferrite system having the general Cu1-xCdxFe2O4
for x=0.0-0.6 have been prepared by using wet chemical co-precipitation method
in air oxidization by taking Cu2+,Cd2+ and Fe3+
cations in their weight proportion. The powders were characterized by XRD, and
hysteresis techniques. For structural characterization the most intense peak
(311) of XRD patterns were considered. The particle size obtained from XRD data
was found in the range 25-26nm. The magnetic properties were investigated by
using room temperature pulse field hysteresis loop technique. The saturation
magnetization (Ms) increases with cadmium concentration ‘x’ up to x=0.3 and
thereafter it decreases.
Keywords: Structural properties, magnetization, particle
size.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.13 NCNA-19
The samples of MgZnxMnxFe2-2xO4
spinel ferrite systems with varying x [x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 and
0.6] were synthesized by double sintering ceramic method. A. R. grade oxides of
magnesium, zinc, manganese and ferric were used for the preparation of MgZnxMnxFe2-2xO4
ferrite. All the synthesis powders were characterized by using X-ray
diffraction (Philips X-ray diffractometer, Model PW3710) technique at room
temperature. The X-ray diffraction patterns were recorded in the 2q range of 200-800
using Cu-Ka radiation. The magnetic properties were measured using pulse field
technique provided by Magneta company.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.14 NCNA-19
This article describes the dielectric properties of CuO/ZnO nanocmposite
synthesized by mechanical milling method. The three samples are prepared in
1:1, 1:2 and 2:1 weight ratio of CuO and ZnO. The dielectric properties of
three samples were investigated at 1MHz, 10MHz and 100MHz frequency in
temperature range 0 to 1000c. The broadband dielectric spectroscopy
(BDS) is used for investigation of dielectric properties. The comparative study
of three samples of CuO/ZnO nanocomposite was done and it was concluded that
dielectric constant ε improves with increase in CuO weight percentage in
sample. Also it rises with rise in temperature.
Keywords: Nanocomposite, dielectric constant, broadband
dielectric spectroscopy.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.15 NCNA-19

The classification of Microwave Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) image has
become a very important task after availability of data from satellites. In
this paper Microwave C-band Dual Pole SIR-C SAR satellite dataset of Pinatubo,
Philippines is used. Here unsupervised and supervised classification techniques
applied on the dataset used. The unsupervised classification techniques include
like H-alpha, Wishart H-alpha and Wishart H-A-alpha, whereas in supervised
classification classes, made manually, using clustering process. The aim of
this work finds the vegetation present in the selected SAR images using above
mentioned classification techniques. This paper presents the comparison of the
simulation results of both classification techniques for the analysis of area
coverage by Vegetation. In supervised classification, the classified image is
better than all unsupervised classification techniques.
Keywords:
SAR, SIR-C, Unsupervised,
Supervised Classification.
SPECIAL ISSUE FEB 2019 PUNE RESEARCH TIMES (IPRP-2019 & NCNA-2019)
1.16 NCNA-19

In
this article, we report the structural characterization and the results on mass
attenuation coefficient, total atomic cross-section and total electronic
cross-section of Ni0.3Zn0.5Cu0.2Fe2O4
spinel ferrite multi-elemental composite.. The structural
characterization of Ni0.3Zn0.5Cu0.2Fe2O4
ferrite composite was carried out by X-ray diffraction technique. The X-ray
analysis confirmed the formation of single phase cubic spinel structure. The
mass attenuation coefficient, total atomic cross section and total electronic
cross-section of Ni0.3Zn0.5Cu0.2Fe2O4
spinel ferrite have been obtained using narrow beam technique as a function of
varying thickness. The results show that as thickness increases all these
parameters decreases. XCOM program was used to obtain the theoretical values of
mass attenuation coefficient.